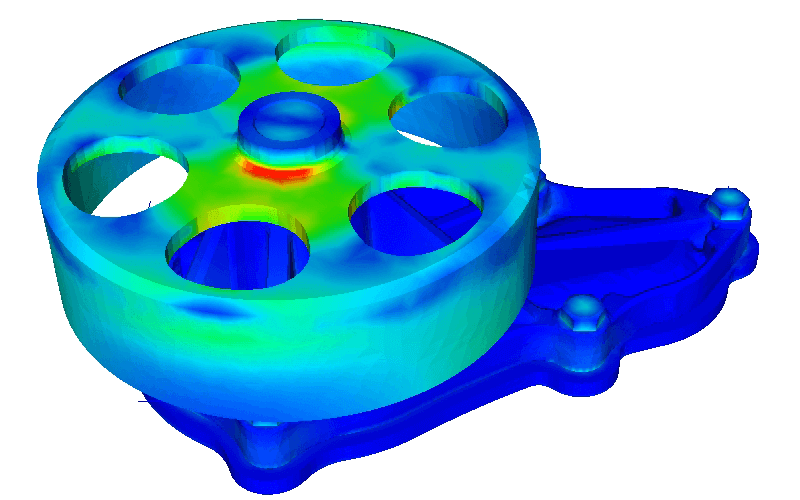
Computer aided engineering (CAE) techniques provide the means to cope with the demand for increased productivity of more sophisticated and reliable product design and manufacture.
Finite element analysis (FEA) is a technique used to validate the design. Using an approximate numerical technique called the Finite element method, FEA is typically used by engineers in the CAE and R&D departments.
FEA has become part of the product development cycle in many industries including automotive, aerospace, earth moving and construction equipment, and bio-medical.
Primary Steps in FEA
- Understanding the physical problem
- Selection of type of analysis and Generation of elements (sheet metal parts, castings, different kinds of joints - revolute, bolted and weld)
- Defining material (isotropic, anisotropic, hyper-elastic) and sectional properties, applying loading conditions and constraints
- Solve the equations and Post processing of results
- Present the results to the designer with conclusions and appropriate design suggestions